Techniques
Techniques: Electronic Structure, Magnetism and Dynamics
As part of the continuous renewal of ESRF capabilities, the techniques may change over time. This page represents a snapshot of the technique portfolio of the Electronic Structure, Magnetism and Dynamics Group as of 2015.
- X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS)
- X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) or Near edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS)
- Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS)
- High-energy resolution fluorescence detected (HERFD) or partial fluorescence yield (PFY) XAS
- Dichroism
- X-ray linear dichroism (XLD)
- X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD)
- X-ray magnetic linear dichroism (XMLD)
- X-ray natural circular dichroism (XNCD)
- X-ray magnetochiral dichroism (XM
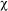 D)
D) - Non-reciprocal X-ray magnetic linear dichroism (NR-XMLD)
- X-ray detected magnetic resonance (XDMR)
- Inelastic X-ray scattering (IXS)
- Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS)
- X-ray emission spectroscopy
- X-ray Raman scattering (XRS)
- Polarization analysis
Sample environment
- Extreme conditions
- High pressure XAS
- High pressure magnetic studies
- High magnetic fields (static and pulsed)
- High temperature (laser heating)
- In-situ studies
- Electrochemical cells
- Catalysis cells (1000o C under controlled gas environment)
- Gas mass flow controllers
- Mass spectrometer
- Liquid jet



