- Home
- Users & Science
- Find a beamline
- Structure of materials
- ID22 - High resolution powder diffraction beamline
- Science at ID22
- Examples: Non-crystalline materials
Examples: Non-crystalline materials
Here you will find a cross-section of PDF studies carried out on the beamline. Experiments were carried out on ID22 (since 2014), and ID31 (2002 - 2013). Examples include:
- ZrW2O8
- Semiconducting selenium nanoparticles
- read more about the session on total scattering form powder diffraction at EPDIC-10
ZrW2O8
A recent study [1] of ZrW2O8, investigated the amorphous phase that can be recovered after its high-pressure amorphization transition above 1.5 GPa. Reverse Monte Carlo modelling of neutron and ID31 data shows that the large increase in density on pressurising is accommodated within the structure by increased bonding between the WO4 tetrahedra. This increases the tungsten coordination; postulated changes to the ZrO6 octahedral environment are not required. This densified crystal based model, which contains significant local disorder within a distorted periodic structure, was also in keeping with data measured in situ at high pressure.
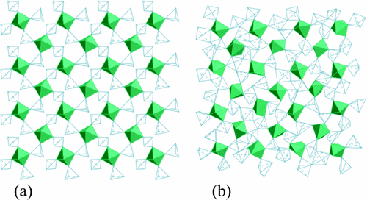
Figure 1: Polyhedral representation of a section of (a) α-ZrW2O8 and (b) amorphous ZrW2O8 from RMC refinement of model B [1].
[1] Structural Description of Pressure-Induced Amorphization in ZrW2O8. D. A. Keen, A. L. Goodwin, M. G. Tucker, M. T. Dove, J. S. O. Evans, W. A. Crichton, and M. Brunelli, Phys. Rev. Lett., 98, 225501 (2007).
(top)
Semiconducting selenium nanoparticles
Combining Rietveld analysis with PDF analysis can be advantageous for crystalline materials with short-range order representing deviations from the average (crystallographic) structure. Thus the structural properties of semiconducting nanoparticles of selenium grown in the pores of a neodymium zeolite-Y were investigated using this approach [2]. Powder diffraction patterns were measured at 41 keV (0.298 Å) up to 110° in 2θ and the average structure refined, which included three Se sites forming a cluster in the large (13 Å diameter) cavity of the zeolite. The clusters however contain vacancies, and relaxation in the Se positions is then expected. Indeeed the Se atoms had large temperature factors in an attempt to model this disorder.
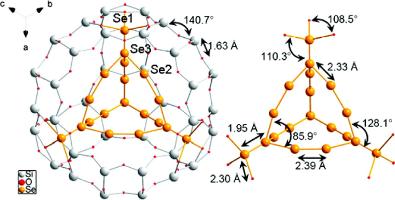
Figure 2. (left) Rietveld fit and (right) average structure of Se nanoparticles in Nd-zeolite-Y, [6].
According to the chemical composition, 32% of the cages can be filled. PDF analysis, which includes the evident diffuse scattering from short-range order, indicated that the average structure was adequate on the length scale from 8 - 50 Å, suggesting that correlations between clusters in adjacent cages via the framework are not important. On the 1 - 8 Å scale however, deviations from the average structure are evident. The PDF was used to extract a model of the short-range order within the Se clusters, and to account for correlations between the Se clusters and the framework, which can relax under the influence of the clusters.
[2] From average to local structure: A Rietveld and an atomic pair distribution function (PDF) study of selenium clusters in zeolite-NdY. Abeykoon A.M.M., Donner W., Brunelli M., Castro-Colin M., Jacobson A.J., Moss S.C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 13230, (2009).
(top)
References:
[1] Structural Description of Pressure-Induced Amorphization in ZrW2O8. D. A. Keen, A. L. Goodwin, M. G. Tucker, M. T. Dove, J. S. O. Evans, W. A. Crichton, and M. Brunelli, Phys. Rev. Lett., 98, 225501 (2007).
[2] From average to local structure: A Rietveld and an atomic pair distribution function (PDF) study of selenium clusters in zeolite-NdY. Abeykoon A.M.M., Donner W., Brunelli M., Castro-Colin M., Jacobson A.J., Moss S.C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 13230, (2009).
- ID22 User Guide
- Industrial Users
- Scientific Applications of ID22
- Examples of structural studies on ID22
- Examples of dynamic and in-situ studies on ID22
- Examples of Microstructure on ID22
- Examples of residual strain studies on ID22
- Sample Environment on ID22
- ID22 technical description
- ID22 publications and reports
- ID22 Contacts



