- Home
- News
- Spotlight on Science
- New Opportunities...
New Opportunities at ID10B: High Energy for Surface Studies at Liquid/Liquid Interfaces
21-04-2005
Share
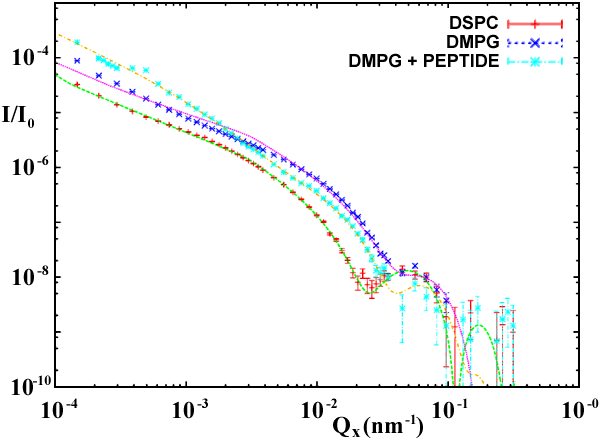
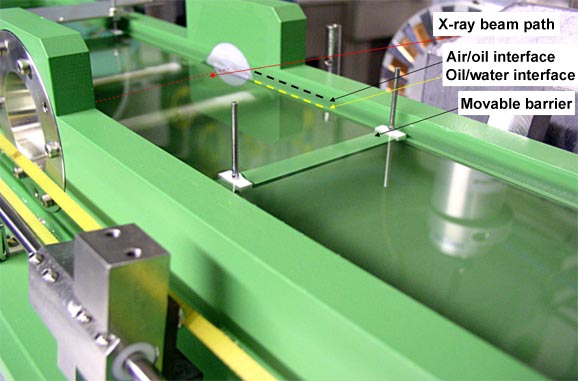
The recent upgrade of the ID10B optics expands the available energy range to 22 keV. This allows studying buried interfaces (solid/liquid and in particular liquid/liquid), which play an important role in many biological processes. Experiments on such interfaces require a high energy as the X-ray beam is absorbed on its way through the liquid. For the first time at the ESRF, this has allowed us to apply all possible surface scattering techniques to an organic monolayer formed at the interface of liquid hexadecane and water. In this way the specular reflectivity signal, off-specular and diffuse scattering spectra were obtained. Figure 1 shows diffuse scattering (symbols) and the best fit (lines) measured at a grazing angle below the critical angle of total reflection at a hexadecane/water interface for 1) monolayer of phospholipids DiStearoyl-PhosphatidylCholine - DSPC, 2) monolayer of phospholipids DiMiristoy- PhosphatidylGlycerol - DMPG and 3) monolayer of DMPG in the presence of an antimicrobial peptide Peptidyl-Glycyl-Leucine-carboxyamide - PGLa. From these data the vertical electron density profile of the film and its elastic constants were obtained. Bending rigidity of the films expressed in the units of KBT is 40 for DSPC, 30 for DMPG and 10 for DMPG with peptides. Difference in rigidity between DSPC and DMPG can be explained by the difference in length of the aliphatic chains. The first molecule has 18 hydrocarbon groups while the second has only 14. This difference is seen in the change of van der Waals interaction between molecules and consequently also in the elastic constants. Our results demonstrate that addition of peptides to the negatively-charged membrane of DMPG reduces the rigidity of the film. Figure 2 shows the Langmuir-trough constructed for such studies.
 |
|
Fig. 2: Langmuir trough for studying Liquid/Liquid interface. |
Authors
O. Konovalov (a), E. Saint-Martin (a), J. Daillant (b), D. Luzet (b), V. Padmanabhan (b)
(a) ESRF
(b) CEA, Saclay-SCM/LIONS (France)